Today, the need for real-time visibility into the location of physical assets, devices, and people is more critical than ever. Organizations across industries, from healthcare to logistics, are striving to optimize operations, enhance security, and improve efficiency by knowing the precise location and movement of their key resources. Whether it’s managing inventory in a warehouse, tracking patients in hospitals, or ensuring seamless operations in hybrid workplaces, leveraging technology to gain actionable insights has become a top priority.
Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) tracking has emerged as a modern, scalable solution to address this challenge. BLE uses low-power wireless communication to enable real-time tracking of objects, people, or devices with precision. It’s a versatile technology that is increasingly being utilized in environments such as smart buildings, hybrid workplaces, and healthcare facilities. As organizations continue to seek reliable and cost-effective tracking solutions, the adoption of BLE is poised to accelerate, with significant advancements expected by 2025.
What Is BLE Tracking?
BLE tracking refers to the use of Bluetooth Low Energy signals emitted by small devices, such as beacons or tags, to monitor the location and movement of objects or people within a defined area. These tags are often attached to items or carried by individuals, while fixed readers or access points receive the transmitted signals to determine their positions. BLE is widely praised for energy efficiency, as devices can operate for months or even years on a small battery. This makes it an ideal choice for large-scale tracking needs.
BLE tracking is particularly effective in indoor environments where GPS signals are unreliable. Examples are multi-floor buildings, warehouses, hospitals, or office spaces. BLE-enabled devices broadcast low-power signals at regular intervals, and nearby readers capture these signals to calculate the location of the tagged object or person. The resulting data is processed through software systems to provide real-time visibility and actionable insights. This enables accurate indoor tracking with scalability and cost efficiency.
How BLE Tracking Works
BLE tracking relies on three key components to function:
- BLE Tags or Beacons: Small, battery-powered devices that act as transmitters, periodically emitting Bluetooth Low Energy signals.
- BLE Readers or Receivers: Devices such as access points (APs) or gateways that detect these signals and relay the data to a central processing system.
- Software Platform: A cloud-based dashboard or location engine that processes this data, visualizes the location of assets or people, and provides actionable insights.
For example, a BLE tag attached to a laptop transmits a signal every few seconds. Nearby Wi-Fi access points pick up the signal and forward it to a location engine. The engine then maps the laptop’s location within the building and can trigger alerts if it moves outside a designated area. This ensures real-time visibility and enhances operational control.
Key Benefits Of BLE For Indoor Positioning
1. Real-Time Asset Visibility
One of the key advantages of BLE asset tracking systems is their ability to provide real-time visibility into the location and status of assets. By deploying BLE tags or beacons on assets and integrating them with a centralized, cloud-based tracking system like Cisco Spaces, businesses can effortlessly monitor the movement of assets throughout their indoor spaces. This real-time visibility enables organizations to quickly locate assets, optimize resource allocation, and reduce the time spent on searching for misplaced or lost items.
2. Accurate Asset Tracking
BLE asset tracking offers high-accuracy tracking of assets within indoor environments. With the use of precise positioning algorithms and multiple BLE beacons strategically placed throughout the facility, Cisco Spaces can achieve highly accurate asset localization. This level of accuracy ensures that organizations have precise information regarding the whereabouts of their assets.
3. Streamlined Inventory Management
Efficient inventory management is critical for organizations to avoid stock depletion, optimize asset utilization, and reduce unnecessary purchases. BLE asset tracking simplifies inventory management by providing real-time inventory updates and automating inventory reconciliation processes. With the ability to identify low stock levels, track asset utilization patterns, and generate automated reorder alerts, businesses can streamline their inventory management workflows and make data-driven decisions.
4. Proactive Maintenance
Maintaining assets in optimal condition is vital for ensuring smooth operations and minimizing downtime. BLE asset tracking systems enable businesses to implement proactive maintenance strategies by providing valuable insights into asset usage patterns and performance metrics. Asset usage data can help schedule preventive maintenance, track equipment lifecycle, and reduce the risk of unexpected breakdown or failure.
5. Security for High-Value Assets
Ensuring the security of high-value assets is a top priority across industries. Asset tracking systems offer enhanced security features by enabling organizations to receive instant alerts if assets are moved beyond designated areas. This proactive security measure helps prevent theft, unauthorized access, and loss of assets.
Top Industry Use Cases for BLE Tracking in 2026
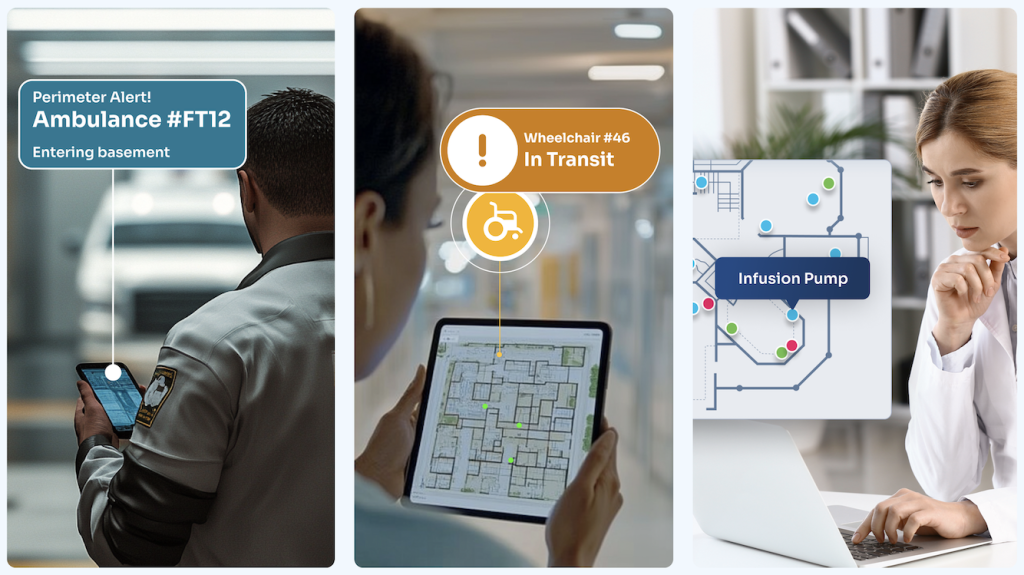
Hospital Equipment & Staff Tracking
BLE tracking is widely used in hospitals to monitor the location of essential medical equipment, in real time. This can include infusion pumps, wheelchairs, and defibrillators. By attaching BLE tags to equipment and personnel, healthcare facilities can significantly reduce search times, improve equipment utilization rates, and ensure faster response during critical emergencies. This technology enhances operational efficiency and improves patient care outcomes in high-pressure hospital environments.
Corporate IT Asset Tracking
Companies are leveraging BLE to track IT assets such as laptops, mobile devices, and audio-visual equipment by attaching BLE tags and integrating them with Wi-Fi networks. This enables real-time zone-based monitoring, preventing asset loss or theft while providing better visibility across sprawling office campuses. BLE tracking also aids in automating inventory management and improving the overall security of organizational IT infrastructure.
Warehouse & Logistics Management
In warehouses and logistics facilities, BLE is used for efficient tracking, inventory management, and automating location-based tasks. By tagging materials and pallets with BLE beacons, organizations can track real-time material movement and inventory levels across large facilities, ensuring seamless operations. This technology reduces errors, optimizes workflows, and provides end-to-end visibility into supply chain processes to enhance productivity.
Smart Workplace Occupancy & Experience
BLE plays a key role in optimizing workplace experience. It does this by enabling features like room occupancy monitoring, hot desking, and employee location analytics. For instance, BLE devices can be used to track how employees utilize office spaces, helping organizations implement smarter layouts and improve resource allocation. Platforms like Cisco Spaces ingest BLE data to provide actionable insights into smart building operations and enhance the overall employee experience, without compromising privacy.
How to Implement BLE Solutions
1. Define Goals & Project Scope
Begin by clearly defining the goals of your BLE implementation project. Identify the specific challenges you aim to solve, such as improving asset visibility, enabling indoor wayfinding, or optimizing occupancy monitoring. Frame the project scope based on your use case, available budget, and desired timeline. It could be a small-scale pilot, a single-floor deployment, or an enterprise-wide rollout. Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) early. These can include reducing lost equipment, improving utilization, or increasing operational efficiency. They can involve cross-functional stakeholders like IT, operations, security, and facilities teams, to ensure alignment and success.
2. Evaluate Infrastructure Requirements
BLE tracking systems can leverage either dedicated BLE readers or existing Wi-Fi access points that support BLE functionality, such as Cisco Meraki or Catalyst devices. Start by auditing your current infrastructure to ensure BLE compatibility and determine if any coverage gaps or cabling updates are needed. Consider the level of precision you require—zone-level tracking (e.g., floor or building) may suffice for general applications, while more precise room-level tracking (e.g., specific treatment rooms or offices) may be critical for certain use cases. BLE solutions can scale effectively, from small departmental pilots to enterprise-wide deployments, with thoughtful infrastructure planning.
3. Plan the Deployment & Maintenance
Carefully plan the physical deployment of BLE beacons or tags, ensuring their placement accounts for zone definitions, floor plans, and signal strength to optimize coverage. Start with a small pilot area to validate tracking accuracy and fine-tune the system before scaling to larger deployments. Proactively plan for tag maintenance, as BLE tags typically last one to three years, depending on their signal interval. Assign clear responsibilities for ongoing maintenance tasks, such as replacing tag batteries, re-tagging assets, and recalibrating where necessary, to ensure long-term system reliability.
4. Integrate With Existing Systems
To maximize value, integrate BLE tracking data into your existing technology stack, such as asset management systems, electronic medical records (EMRs) in healthcare, building management systems, or IoT dashboards like Cisco Spaces. Select platforms that support open APIs and data export capabilities to ensure interoperability and seamless data flow between systems. Be mindful of privacy and security—implement role-based access controls, ensure data anonymization, and maintain audit logging to protect sensitive information. Additionally, ensure compliance with internal data governance policies and regulations like GDPR when tracking staff or visitors.
5. Create Change Management & User Training
User adoption is critical to the success of any BLE solution. Provide customized training to end users based on their roles, such as training for administrators on platform usage and alert configuration, IT teams on infrastructure maintenance, and frontline staff on use cases like equipment retrieval. Offer visual onboarding aides, FAQs, and documentation to improve system usability and address common questions. Create a feedback loop during the rollout to gather insights on the user experience and identify areas for improvement, enhancing both adoption and system efficiency.
6. Ensure Privacy & Security
Implement robust privacy and security practices to address concerns about tracking people and devices, including ensuring consent, anonymizing data, and providing granular data access controls. Cisco Spaces, for example, offers enterprise-grade encryption, role-based access policies, and advanced access controls to safeguard sensitive information. Work closely with legal and compliance teams from the beginning of the project to align privacy workflows with organizational policies and regional regulations, ensuring trust and transparency in the deployment of your BLE solution.
| Take the Cisco Spaces Product Tour Discover how Cisco Spaces makes BLE tracking scalable, secure, and easy to deploy across workplaces, healthcare environments, campuses, and more. No new infrastructure is required. Take the product tour |
Turn BLE Signals Into Business Insights With Cisco Spaces
BLE tracking provides a highly efficient and scalable solution to monitor the location of assets and people within a building. By leveraging real-time and historical visibility, BLE tracking empowers organizations across industries to improve operational efficiency, reduce asset idle time, and enhance safety. Industries such as healthcare, manufacturing, and workplaces benefit from solutions like Cisco Spaces, which facilitate better decision-making, proactive maintenance, and significant cost savings — all through a cloud-based platform.
The relevance of BLE tracking continues to grow as hybrid work models, regulatory compliance, and operational complexities increase. By seamlessly integrating BLE technology with existing Wi-Fi networks, such as Cisco’s Catalyst 9000 and Meraki infrastructure, businesses can implement cutting-edge solutions without the need for major hardware upgrades. This capability positions BLE as a future-proof technology for organizations seeking smarter asset management and location insights.
Take the next step and see BLE tracking in action with Cisco Spaces. Start the product tour to explore how this technology can transform your business.


