Continuous patient monitoring shouldn’t be limited to intensive care units – or require hospitals to deploy yet another layer of infrastructure. At Cisco, we’ve reimagined how medical wearables connect, scale, and deliver outcomes across general wards and peri-hospital environments. Working with North Carolina State University, wearable innovators like Corsano, and multiple healthcare providers across Europe, Cisco has enabled a more efficient model for patient care enabling continuous monitoring of patient vital signs outside intensive care environments, allowing medical staff to continuously follow patients, set alarms, and understand trends.
The good news? No new infrastructure needed! Just strap on the wearable and it will communicate directly with your Cisco Wi-Fi 7 Access Points.
Why we innovated
In most hospitals today, patients in general wards are typically checked every four to six hours. For the majority of the day, they remain unmonitored. This gap can delay detection of patient deterioration, introduce errors through manual data entry, and add pressure to already overextended nursing staff – sometimes with serious consequences. This can delay detection of patient deterioration, increase errors from manual data entry, and contribute to overworked nursing staff with sometimes severe consequences. Hospitals also struggle with bed-blocking, as reliable data is needed to safely discharge patients and improve capacity.
Several of Cisco’s healthcare providers felt that they should be able to do better for their patients and their employees. They looked for an innovative solution to solve the problem of monitoring mobile patients in a general ward setting and saw the potential of using battery powered smart sensors of Corsano and others that communicate patient telemetry over a Low Power Personal Area Network (LPPAN), based on Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE).
Early approaches relied on BLE wearables connected to smartphones to collect and transfer patient data for analysis. However, smartphones proved unscalable, and proprietary BLE gateways or USB based dongle inserts proved too costly and complex for hospitals to implement. Our partners needed a single, standards-based, scalable, and secure platform to connect any IoT device to any application.
How we executed
Cisco already delivers a complete end-to-end IOT middleware solution for enterprises with its enterprise-grade wireless infrastructure and Cisco Spaces. However, to deliver a complex patient monitoring outcome, Cisco took on the challenge, working with researcher Muhammed Shahzad of NCSU and his students to build a set of open APIs on top of its wireless infrastructure, that works seamlessly with existing Spaces platform. These APIs enable applications to onboard IoT devices, communicate with them, and receive streaming telemetry from them. This resulted in a solution that essentially turns any Cisco wireless network into a single gateway for non-IP IoT devices. As depicted in the diagram below, this innovative solution called “Sensor Connect for IoT Services” supports any standards-based BLE device and offers three APIs for secure onboarding, device control and data streaming to enable application integration.
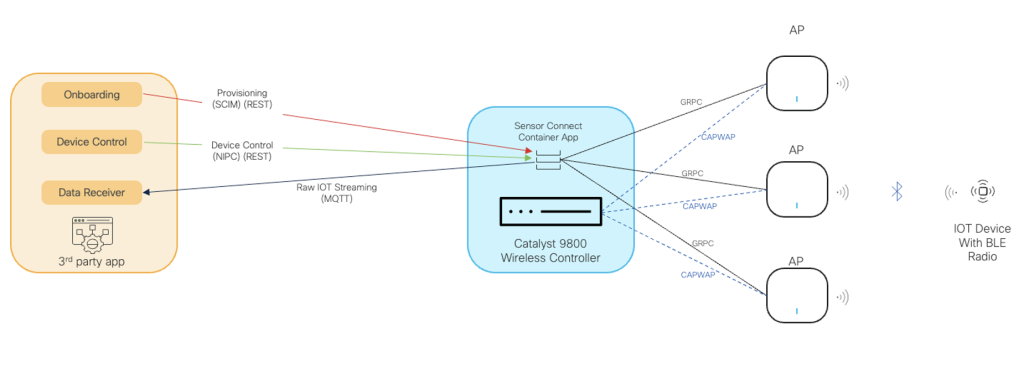
At Cisco we quickly realized we needed to take this one step further. We worked with our partners and the industry to standardize the APIs at the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). This ensures that IoT application providers that develops to these APIs can deploy their application in any enterprise wireless network, regardless of the infrastructure vendor, allowing IoT applications to proliferate in the enterprise. With that, two new proposed standards were born:
- SCIM (System for Cross-Identity-Management) for devices: A standard for onboarding IoT devices (https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/draft-ietf-scim-device-model/), allowing applications to onboard an IoT device to a network
- NIPC (Non-Internet-Connected control of Physical Components): A soon-to-be standard for communicating with non-IP IoT devices (https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/draft-ietf-asdf-nipc/), enabling bi-directional communication and telemetry streaming APIs for devices that do not have the ability to leverage IP-based communication (such as BLE or Zigbee)
What does the solution look like
Corsano became one of the first ecosystem partners to integrate their CardioWatch devices and Health Cloud Application using the Cisco Sensor Connect APIs. Cisco and Corsano jointly conducted a successful Early Field Trial program with several European hospitals to further mature the solution confirming the full stack functionally regarding connectivity (including roaming), onboarding and continues data streaming.
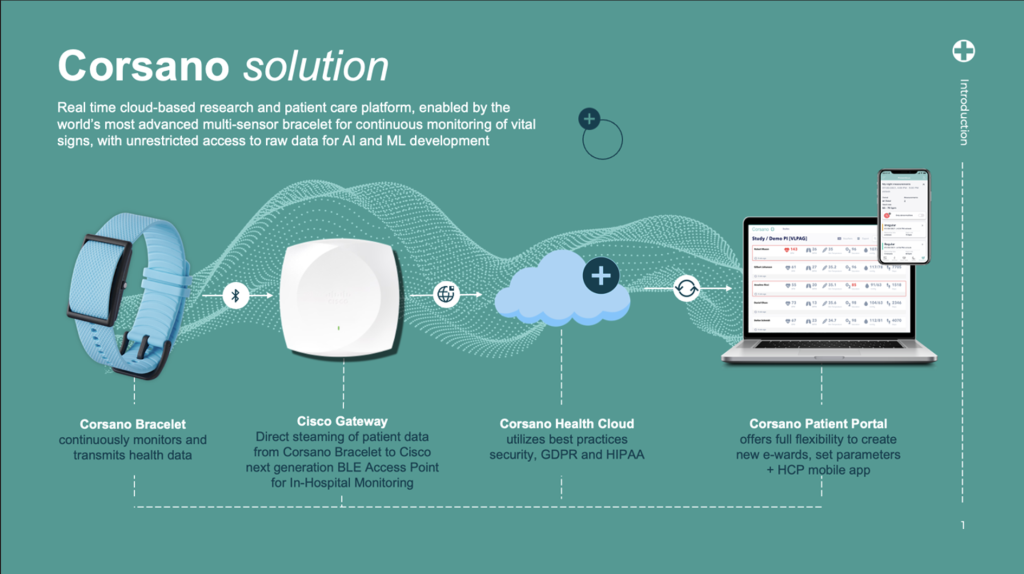
The clinical workflow is simple:
- A nurse scans a barcode on the bracelet, connecting the device to a patient.
- 2.The application provisions the trusted device onto the network and specifies which data streams should be sent to the Corsano patient monitoring application and other destinations, such as the hospital electronic medical record (EMR) system.
- Once powered on, the bracelet automatically connects and onboards to the Corsano Health Cloud.
Revolutionizing Care Pathways
By seamlessly integrating wearable monitoring with hospital networks, Corsano and Cisco enable a new era of healthcare efficiency in Peri-Hospital Care enabling multiple use cases with real outcomes, including:
- Continuous, wireless monitoring for early detection of deterioration in high-risk or post-operative patients and reducing staff workload.
- Post-Surgical & Inpatient Recovery. Assesses recovery progress, helps prevent complications and supports early discharge decisions
- Real-Time Vital Signs Monitoring: Allows rapid triage, treatment prioritization, identification of shock, hypoxia, or cardiac distress in chaotic environments like an emergency room.
Excited about the possibilities and outcomes?
Cisco Spaces Sensor Connect is a horizontal technology in a field with many specialized devices. You can try all of this with your existing WiFi7 deployment with Cisco IOS-XE. Today we support BLE, but the architecture is designed to adapt to other layer 2 technologies. It is built to be able to seamlessly integrate with Cisco Spaces for a truly unified IOT architecture for all partners to develop with. Documentation is available on cisco.com:
- Cisco DevNET coding examples and supported hardware and software
- Cisco Sensor Connect for IoT Services Configuration Guide
- API Reference Guide
Contact your Cisco salesperson for more information.



